Are you planning to buy a company? Well, whether you’re a first-time entrepreneur, or a budding business enthusiast, the prospect of buying an existing business is an exciting yet intricate journey. Navigating the process with confidence requires a well-crafted roadmap.
Let’s understand with live CASE STUDY.
Meet Amit (name changed), a professional based in London, UK, with a stellar background – he’s a qualified chartered accountant, holds an MBA from a prestigious university, and boasts over 10 years of experience in a multinational tech firm. Despite his successful career, Amit is drawn to the allure of entrepreneurship. His motivation? The promise of financial independence, creative freedom, and the opportunity to pursue his passions.
For individuals like you and Amit, the journey of becoming a business owner is about more than just financial gains. It’s a path paved with ambition and innovation, a chance to make a significant impact on the world.
Now, as you consider taking the plunge into entrepreneurship, you face a choice: start your venture from scratch or buy an existing business. Both options come with their set of advantages and challenges, as we’ll explore in the image below.
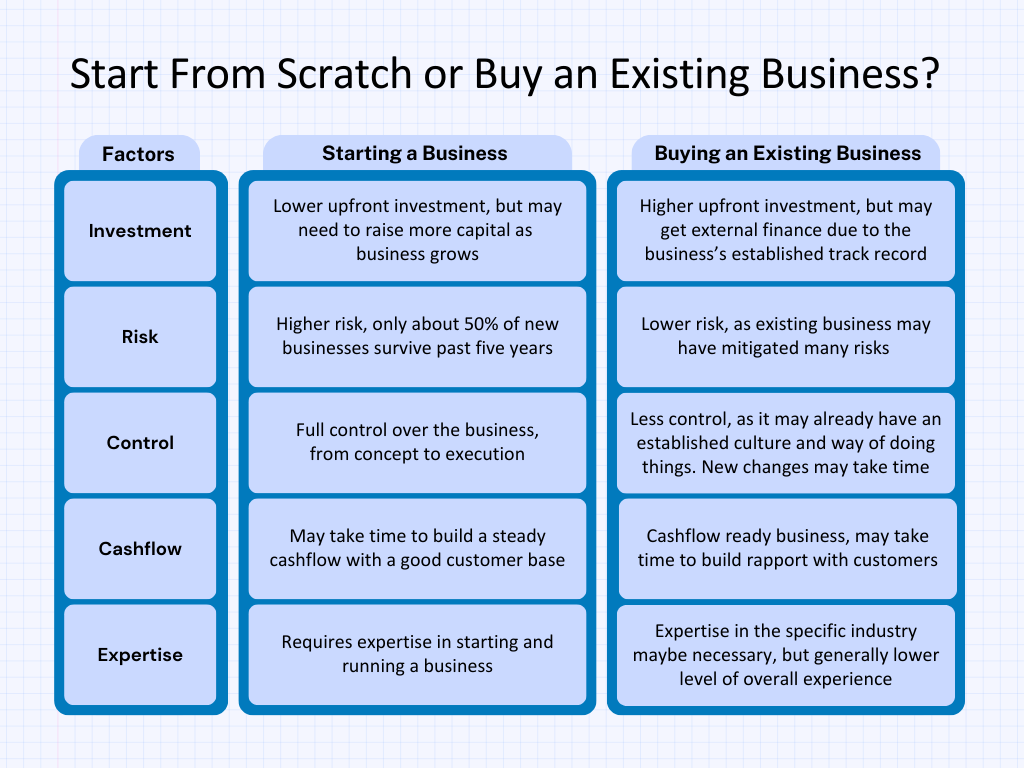
With above infographic, you can understand, why most of the seasoned professionals and first-time entrepreneurs like you are preferring to acquire an existing business instead of starting from scratch.
Now, the QUESTION is How to Buy a Business?
To solve this puzzle, our experienced investment bankers prepared this ultimate guide and tried to cover everything from essential insights to valuable tips to help you get clear picture of how to buy an existing business. We’ll delve into step-by-step to provide detailed guidance to ensure your acquisition journey is a seamless path to success.
Here are the top 10 steps to buy existing business successfully and start your growth journey in 2024.
Step 1: Clarify Your Vision for Business
Before venturing into business acquisition, it is essential to set out your vision. A clear vision acts as a filter, eliminating businesses that don’t align with your aspiration
Set Out Your Goals and Objectives:
- Outline the overall goals and objectives you hope to accomplish through owning a business. Do you hope for financial success; greater work-life balance; or the chance to make an impactful difference in an industry or something else?
Step 2: Acquiring an Existing Business Checklist
When you’ve got your vision clear your next step is creating a checklist that will help you along your journey.
1. Financial Status:
- Review your current financial condition and create a budget for any acquisition, including the initial capital requirement as well as working capital for a period of 1-2 years.
2. Industry Selection:
- Pick the industry that best matches your preferences, skills and longer-term goals.
3. Personal Strengths and Weaknesses:
- Evaluate your individual skills and strengths and consider how they could be leveraged within a business setting.
4. The Goals and Objectives:
- Set specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your new venture.
Step 3: Where to Find Businesses for Sale
After you have your checklist in place now is the time to identify business opportunities for your growth journey:
1. Online Marketplaces:
- If you are planning to acquire business in India, platform like IndiaBizForSale is on to go to find businesses that are operating and are available for sale from India. You can also check bizbuysell, businessesforsale, acquire for global businesses.
2. Classified Ads:
- Watch out for classified ads in local newspapers as well as business publications. This can help you get connected with the businesses seeking exit from their venture (It’s hard to find but you can try it).
3. Business intermediaries:
- Make use of the knowledge of expert investment bankers such as IBGrid.com Team who specialize in successful M&A transactions.
4. Industry Associations or Forums:
- Join industry-specific associations or forums for accessing exclusive listings and networking with potential sellers.
Step 4: Primary Vetting
The focus is on quickly evaluating the target company to determine if it’s worth pursuing further. The primary vetting process aims to identify potential deal-breakers and filter out unsuitable candidates. Here’s what the primary vetting process should focus on:
1. Financial Review:
- Request high-level financial statements and assess revenue trends, gross margins, and profitability.
- Look for any alarming financial issues such as consistent losses or significant fluctuations.
2. Legal and Compliance Check:
- Review the target company’s legal structure, contracts, and any pending legal disputes.
- Check for compliance with basic regulatory requirements in the industry.
3. Operational Assessment:
- Understand the company’s core operations and key processes.
- Identify any major operational challenges that could impact the acquisition.
4. Market Positioning:
- Gather basic information about the target company’s market presence, competitors, and customer base.
- Evaluate if the company’s products or services align with the acquiring company’s strategic goals.
5. Management Team:
- Gain a brief understanding of the key executives and their roles.
- Assess the stability and experience of the management team.
6. Key Relationships:
- Identify major customers, suppliers, and partners.
- Evaluate the strength of these relationships and their impact on the business.
7. Intellectual Property (IP) Overview:
- Get a general sense of the company’s intellectual property assets, such as patents and trademarks.
- Look for any obvious issues related to IP ownership or infringements.
8. Employee Overview:
- Understand the size of the workforce and any notable HR issues.
- Evaluate the general employee satisfaction and retention rates.
9. Initial Synergy Check:
- Determine if there are any immediate synergies or alignment with the acquiring company’s objectives.
10. Risks and Red Flags:
- Look for any obvious red flags, such as negative reviews, customer complaints, or major legal troubles.
- Identify potential deal-breakers or areas that require further investigation in the full due diligence phase.
The primary vetting process is about quickly gathering essential information to make an initial assessment. If the target company passes this initial screening, a more comprehensive due diligence can be conducted after signing the LOI and dedicating additional resources.
Step 5: Valuing the Business
Understanding diverse business valuation techniques is crucial:
1. Asset-Based Valuation:
- Suitable for asset-heavy, growing, and profitable businesses. Comparable methods work well here.
2. Income-Based Valuation:
- For businesses with strong cash flows. Consider methods like the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method.
3. Market-Based Valuation:
- Involves assessing market multiples and transaction comparable methods, ideal for various business types.
4. Replacement Cost Method:
- Appropriate for asset-heavy but stagnant businesses, focusing on the cost of replacing assets.
5. Professional Guidance:
- To ensure you are not overpaying, seek expert advice from experienced business valuation experts, if required. An intermediary will check the business opportunity dispassionately and would help you arrive at a range at which you can negotiate and help you avoid overpaying or losing a good deal because of undervaluing a business.
Step 6: Negotiating the Deal (Signing of LOI)
In this step, you can cover the negotiation process in more detail, focusing on how to navigate the conversations with the seller effectively. Here’s a brief outline for Step 6:
1. Preparation for Negotiation:
- Prepare for negotiation by gathering all necessary information about the business and understanding your own goals and limitations. You can compare the transaction vs your buy-side thesis you built earlier and check for any significant gaps.
2. Seeking Professional Guidance:
- Discuss when and why you might need professional advisors, such as lawyers or business brokers, to assist in the negotiation process.
3. Key Terms and Conditions:
- Highlight the critical aspects of the deal to negotiate, including the sale price, payment structure, non-compete agreements, and any contingencies.
4. Maintaining Communication:
- Stress the importance of maintaining open and constructive communication with the seller throughout the negotiation process.
Step 7: Securing Financing
When the worth of the company is established, you should consider the best way to finance its acquisition
1. Financing Options:
- Look at the various options for financing, including bank loans or personal financing.
2. Interest Rates and Repayment Terms:
- Check out the rates of interest and repayment terms for each financing option prior to making a decision.
3. Financial Planning:
- Determine if the method you select for financing is compatible with your overall financial plan as well as cash flow forecasts.
Step 8: Due Diligence
A thorough due diligence (DD) process in the context of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) involves a comprehensive investigation into various aspects of the target company. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the items typically covered during a thorough due diligence:
1. Financial Due Diligence:
- Financial Statements: Detailed review of balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
- Financial Ratios: Analysis of profitability margins, liquidity ratios, and efficiency ratios.
- Historical Performance: Examination of past financial performance and trends.
- Revenue Recognition: Evaluation of revenue sources, contracts, and recognition policies.
- Outstanding Liabilities: Assessment of debts, pending lawsuits, and contingent liabilities.
- Taxation: Examination of tax compliance, liabilities, and potential tax risks.
2. Legal and Compliance Due Diligence:
- Contracts and Agreements: Review of customer contracts, supplier agreements, leases, and other legal commitments.
- Intellectual Property: Detailed examination of patents, trademarks, copyrights, and licenses.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assessment of industry-specific regulations, permits, licenses, and compliance records.
- Litigation and Legal Issues: Identification of ongoing or potential legal disputes and litigation history.
- Insurance Policies: Review of insurance coverage and liabilities.
3. Operational Due Diligence:
- Supply Chain: Evaluation of suppliers, logistics, and potential risks in the supply chain.
- Production and Processes: Assessment of production methods, operational efficiency, and capacity.
- Technology and IT Systems: Examination of technology infrastructure, software, and cybersecurity measures.
- Employee and HR: Review of employment contracts, organizational structure, and HR policies.
- Customer Relationships: Analysis of key customer relationships, satisfaction levels, and customer retention strategies.
4. Market and Competitive Due Diligence:
- Market Analysis: Evaluation of market size, growth trends, and market segmentation.
- Competitive Landscape: Assessment of competitors, market share, and unique selling propositions.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering customer feedback, reviews, and complaints for market perception analysis.
5. Strategic and Synergy Due Diligence:
- Strategic Fit: Examination of how the target company aligns with the acquiring company’s strategic goals.
- Synergy Analysis: Identification of potential synergies, cost-saving opportunities, and revenue enhancements post-acquisition.
6. Environmental and Sustainability Due Diligence:
- Environmental Compliance: Assessment of environmental impact, compliance with environmental regulations, and potential environmental liabilities.
- Sustainability Practices: Evaluation of sustainability initiatives, green technologies, and corporate social responsibility.
7. Cultural Due Diligence:
- Organizational Culture: Assessment of company culture, values, and alignment with the acquiring company’s culture.
- Employee Morale: Understanding employee satisfaction, retention rates, and overall organizational health.
A thorough due diligence process involves a deep dive into these areas, often requiring collaboration between financial experts, legal advisors, industry specialists, and other professionals. Conducting meticulous due diligence is essential for making informed decisions and mitigating risks associated with the acquisition. Ideally you should seek help from a professional DD agency to conduct this for you, and generally this agency is not the same intermediary who you use to help in M&A.
Step 9: Closing the Deal
Congratulations on nearing the deal closure! In this step, customize your approach based on the transaction’s unique needs:
1. Finalize Legal Matters:
- Thoroughly review legal documents, ensuring accuracy. Seek legal advice to address complexities and mitigate risks.
2. Transition Planning:
- Develop a detailed transition plan, fostering open communication with employees, customers, and suppliers. Minimize disruptions and ensure a seamless transfer of ownership.
3. Implementation Strategy:
- Gradually execute your business plans, adapting to evolving needs. Stay agile and make strategic adjustments as necessary.
4. Re-negotiation (If Needed):
- Address any post-due diligence concerns transparently. Engage in professional negotiations, proposing balanced solutions and documenting agreed-upon changes.
5. Adaptability and Innovation:
- Stay vigilant in the market. Adapt swiftly to changing conditions and innovate to maintain a competitive edge. Continuous improvement is key to long-term success.
Remember, flexibility is vital. Tailoring your approach ensures effective re-negotiations (if required) and a successful transition, setting the stage for a prosperous post-acquisition phase.
Step 10: Success After Acquisition
Now that you are the proud owner of a business venture, your journey has just begun: Top key points to focus on after acquiring an existing business for its continuity and advanced growth outlook:
1. Customer Retention:
- Prioritize customer satisfaction and maintain strong relationships with existing clients. Implement excellent customer service, personalized experiences, and loyalty programs to retain customers. Satisfied customers are more likely to make repeat purchases and recommend your business to others.
2. Employee Engagement:
- Engage and empower your employees. Provide them with training opportunities, recognize their contributions, and involve them in decision-making processes. Engaged employees are more motivated, productive, and loyal, leading to improved customer service and overall business efficiency.
3. Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations and optimize processes to enhance efficiency. Identify bottlenecks, automate repetitive tasks, and invest in technology that improves workflow. Efficient operations reduce costs, increase productivity, and create a strong foundation for growth.
4. Market Expansion:
- Explore strategic avenues for market expansion. Conduct market research to identify untapped opportunities or new customer segments. Consider geographic expansion, diversification of products or services, or strategic partnerships to reach a wider audience. A well-planned market expansion can significantly boost your customer base and revenue streams.
5. Financial Management:
- Maintain a robust financial management system. Monitor cash flow, control expenses, and invest wisely. Financial stability is vital for business continuity and provides the necessary resources for growth initiatives. Regular financial analysis and forecasting help in making informed decisions and mitigating financial risks.
Focusing on these areas ensures a solid foundation for the acquired business, fostering its continuity and enabling strategic growth in the competitive market landscape.
Wrapping Up:
buying an existing company is a proven way to entrepreneurial success, and with this comprehensive guide you’ll be well-equipped to navigate it confidently. No matter if you are an experienced entrepreneur or newcomer; taking advantage of an established company to acquire can fast track your journey.
Note that for any query or concern, you can reach out our 25+ years of experienced Investment Banking Professionals at [email protected]
